EMAIL AT- support@itldigitaltech.com CALL AT- +8801830312344
What is organic Content?
Organic content refers to any type of content created and distributed without paid promotion. This includes blog posts, social media updates, videos, infographics and other types of media that are naturally shared through search engines, social media platforms and other online channels. The primary goal of organic content is to engage audiences, provide value, and build a community around a brand or topic without relying on paid advertising.
Advantages of organic Content
Cost-Effective: Unlike paid advertising, organic content requires minimal financial investment. The main costs are related to content creation and possibly tools for SEO and social media management.
Long-term value: High-quality organic content can attract traffic and engagement long after it’s published. Evergreen content, in particular, remains relevant over time and can consistently attract new audiences.
Builds trust and credibility: Consistently providing valuable, relevant content helps establish your brand as an authority in your industry, building trust with your audience.
Improves SEO: Search engines favor websites that are regularly updated with high-quality content Effective use of keywords, backlinks, and relevant topics can significantly boost your search engine rankings.
Engages and retains customers: Organic content helps build a loyal community. Engaging content encourages interaction and builds a relationship with your audience, increasing customer retention.
Supports Brand Identity: It helps to clearly define and communicate your brand voice and values, differentiating you from competitors.
Types of organic matter
Blog Posts: In-depth articles on topics relevant to your audience optimized for search engines.
Social Media Posts: Updates, photos, videos, stories, and other content shared on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and LinkedIn.
Video: Tutorials, webinars, interviews, and other video content shared on YouTube, Vimeo, and social media platforms.
Infographics: Visual representations of information or data, which are easy to share and understand.
Podcast: Audio content that delivers value through interviews, discussions and storytelling.
Newsletter: Regular email updates that provide customers with valuable information, tips, and insights.
User-Generated Content: Content created by your audience, such as reviews, testimonials, and social media posts that mention your brand.
Best practices for creating organic content
Know your audience: Understand your target audience’s demographics, preferences, and pain points to create content that resonates with them.
Quality over quantity: Focus on creating high-quality content that provides real value to your audience, rather than churning out large amounts of low-quality posts.
SEO Optimization: Include relevant keywords naturally, use meta tags, and make sure your content is structured for readability. Optimize for both search engines and user experience.
Consistency: Regularly update your blog, social media profiles, and other channels to keep your audience engaged and attract new followers.
Engagement: Encourage interaction by asking questions, responding to comments, and engaging with your audience on social media.
Use visuals: Include images, videos, and infographics to make your content more engaging and shareable.
Promote across channels: Share your content across multiple platforms to reach a wider audience Cross-promote between your blog, social media, email newsletters, and other channels.
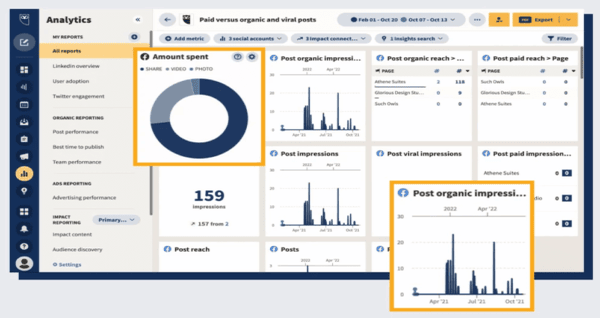
Measure and adjust: Use analytics tools to track your content’s performance. Pay attention to metrics like traffic, engagement, and conversion rates to understand what’s working and adjust your strategy accordingly.
By focusing on these best practices, you can create engaging organic content that not only attracts but also retains and engages your audience, ultimately driving sustainable growth for your brand.

Organic Content vs Paid Content: What's the Difference?
Definition: Organic content refers to any type of content created and distributed without financial investment in promotion. This includes blog posts, social media updates, videos, infographics, podcasts, and other forms of media that gain visibility through natural, unpaid methods.
Key Features:
Cost: Minimal financial investment; Major costs are related to manufacturing materials.
Reach: Relies on search engine rankings, social media algorithms, and audience sharing to reach the audience.
Longevity: Often provides long-term benefits as valuable content continues to attract traffic and engagement over time.
Credibility: Builds trust and authority because it is perceived as more genuine and informative.
Engagement: Focuses on nurturing a community and building relationships with audiences.
Benefits:
Cost-Effective: Requires less financial investment compared to paid materials.
Sustainable Traffic: Can attract ongoing traffic, especially if the content is evergreen.
Brand Loyalty: Increases trust and credibility, contributing to long-term brand loyalty.
SEO Benefits: Improves search engine rankings, and drives organic traffic.
2. Content provided
Definition: Paid content refers to any type of content distributed through paid advertising channels. This includes social media advertising, pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, sponsored content, and other forms of media that require a financial investment for visibility.
Key Features:
Cost: Promotion and placement require a financial investment.
Reach: Targeted advertising can achieve immediate and extensive reach.
Longevity: Usually provides short-term results; Visibility is dependent on ongoing financial investment.
Credibility: Perceived as more promotional, which can sometimes reduce perceived trust.
Engagement: Focuses on immediate conversions and achieving specific marketing objectives.
Benefits:
Immediate Results: Can drive traffic and conversions faster.
Targeted Reach: Allows precise targeting of specific demographics and audience segments.
Scalability: Easily scalable with increased budgets.
Controlled Messaging: Provides control over the timing, placement, and context of messages.
3. Comparison:
Reach:
Organic: Depends on algorithmic visibility and audience engagement. Growth is usually slower but more sustainable.
Paid: Offers immediate and massive reach through targeted campaigns. Effective for quick results.
Cost:
Organic: Low initial cost but requires time and effort to build.
Paying: Requires ongoing financial investment but can be budgeted and scaled as needed.
Credibility:
Organic: Often seen as more authentic and trustworthy.
Paid: It may be perceived as less genuine than advertised.
Engagement:
Organic: Focuses on building a community and building long-term relationships.
Paid: Aim primarily for immediate engagement and conversion.
Longevity:
Organic: Content remains accessible and can attract traffic over time.
Paid: Traffic and engagement decrease when ad spending stops.
Strategic use
Organic Content:
Best for building brand authority, engaging with the community, and improving SEO.
Ideal for long-term growth and maintaining audience relationships.
Content Provided:
Best for launching new products, driving immediate traffic, and achieving quick conversions
Ideal for time-sensitive campaigns and quick reach to specific audience segments.
Conclusion
Both organic and paid content have their unique advantages and are often most effective when used together as part of a comprehensive content strategy. Organic content builds trust and sustainable engagement, while paid content can reach and drive immediate results. Balancing both approaches can help maximize overall visibility, engagement, and conversion rates for a brand.